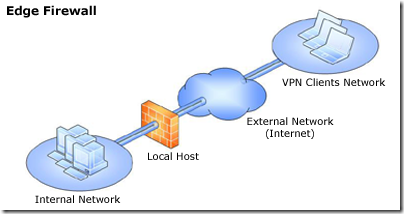
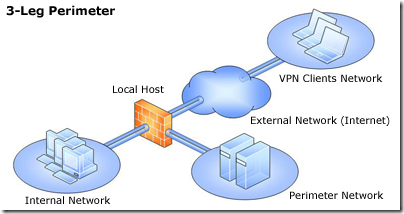
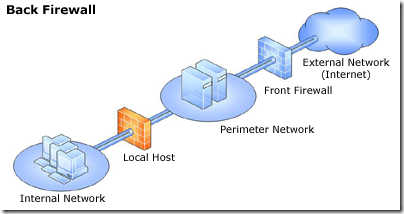
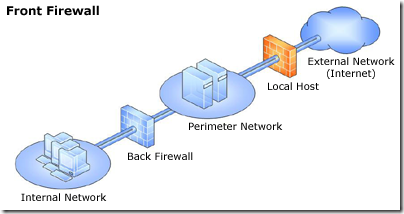
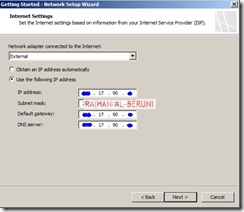
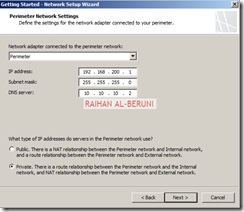
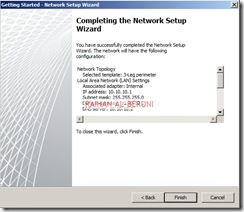
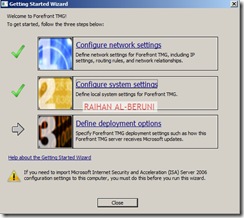
Greetings. We authors of Forefront TMG 2010 Administrator’s Companion are about to finish work on the book, which will be available in January 2010.
To begin giving you a sense of the book, today we’d like to share its Introduction.
Pre-order is available at DigitalGuru; make sure to reserve yours!
Introduction
Forefront Threat Management Gateway Administrator’s Companion is intended to be a functionally usable resource for Forefront TMG 2010 administrators. This admin’s companion is a reference that you’ll want to keep near to hand. The book covers everything you need to learn about and to perform the administrative tasks for Forefront TMG 2010. This book is focused on giving you as much information as possible in a well-organized, clearly written manner.
In short, this book is designed to be the one and only Forefront TMG resource you turn to. To this end, the book zeroes in on common administrative scenarios, frequently performed tasks with documented examples and as many troubleshooting tips as we could fit. One of the goals was to keep the content reasonably concise that the book remains compact and easy to navigate while at the same time ensuring that the book includes as much information as possible—making it a valuable resource. Thus, instead of a lightweight 100-page quick reference, you get a valuable resource guide that can help you quickly and easily perform common tasks, solve problems, and implement advanced Forefront TMG 2010 technologies such as Exchange 2010 publishing, site-to-site VPN management as well as URL Filtering and ISP Redundancy management.
Who Is This Book For?
Forefront Threat Management Gateway Administrator’s Companion covers the Standard and Enterprise editions of Forefront TMG 2010. The book is designed for the following readers:
- Current Forefront TMG 2010 administrators
- Current ISA Server 2004 administrators who want to learn Forefront TMG 2010
- Administrators upgrading to Forefront TMG 2010 from Forefront TMG Medium Business Edition
- Administrators upgrading to Forefront TMG 2010 from ISA Server 2006
- Administrators upgrading to Forefront TMG 2010 from ISA Server 2004
- Managers and supervisors who have been delegated authority to manage Forefront TMG 2010
In order to make the book as understandable as possible, we included some information about basic networking concepts such as IP routing and a discussion of the HTTP protocol and authentication. For those who already possess this knowledge, we’ve placed the bulk of this information in appendices at the end of the book to reduce in-chapter clutter.
We also assume that you are fairly familiar with Windows Server 2008. If you need help learning Windows Server, we recommend that you buy Windows Server 2008 Administrator’s Pocket Consultant or Windows Server 2008 Inside Out.
How Is This Book Organized?
Forefront Threat Management Gateway Administrator’s Companion is designed to provide education about TMG deployment scenarios as much as the features Forefront TMG brings to your firewall deployments. If you are reading this book, you should be aware of the relationship between Pocket Consultants and Administrator’s Companions. Both types of books are designed to be part of an administrator’s library. Pocket Consultants are the down-and-dirty, in-the-trenches books, while Administrator’s Companions are the comprehensive tutorials and references that cover every aspect of deploying a product or technology in the enterprise.
The first two chapters provide an overview of the new edge security products features offered in the Forefront product suite. Chapter 1 discusses the differences between Forefront TMG Medium Business Edition and Forefront TMG 2010. Chapter 2 compares Forefront TMG with Forefront UAG and helps you decide which is more appropriate to your organization’s needs.
In chapters 3 through 7, we cover the various processes involved with evaluating your organization’s requirements and planning your Forefront TMG deployment to support them. These include such factors as determining your traffic profile, mapping your network structure and the Forefront TMG role in that structure; whether it is for edge protection or network isolation. We also outline the upgrade and migration options and considerations for that task.
In chapters 8 through 10, we guide you through actual Forefront TMG installation, installation troubleshooting and provide an introduction to the management console. In chapters 11through 14, we cover basic firewall access policies, network concepts, NIS and various load-balancing methodologies. Chapters 15 and 16 concentrate on the Web proxy and caching concepts.
Chapters 17 through 20 discuss the various forms of traffic protection afforded clients in protected networks, including how these mechanisms interact as well as how to configure, evaluate and troubleshoot them. Chapters 21 through 24 describe various publishing scenarios such as Exchange Web mail, SharePoint and server publishing, outlining the differences and commonalities between them. Each of these chapters offers troubleshooting hints directly related to those scenarios. Chapters 25 through 27 cover VPN concepts and scenarios.
Chapter 28 discusses Forefront TMG logging, including how to use the live and historical log query mechanisms. Chapter 29 covers enhanced NAT; a new feature that allows you to define 1:1 relationships between protected network entities and an IP address in the destination network. Chapter 30 covers Forefront TMG Component Object Model and provides an example of how to automate a common administrative task using VBScript, Jscript and PowerShell.
Chapters 31 through 33 are dedicated to troubleshooting techniques, methodology and tools, with chapter 33 dedicated to using Network Monitor 3. Appendices A through D provide the down-and-dirty discussions around HTTP, authentication, performance monitoring, windows Internet library behaviors as web proxy clients and a detailed dissection of the WPAD script.